Help Contents: |
Close this window |
DSpace captures, distributes and preserves digital research products. Here you can find articles, working papers, preprints, technical reports, conference papers and data sets in various digital formats. Content grows daily as new communities and collections are added to DSpace.
The DSpace content is organized around Communities which can correspond to administrative entities such as schools, departments, labs and research centers. Within each community there can be an unlimited number subcommunities and an unlimited number of collections. Each collection may contain an unlimited number of items.
| BROWSE | top |
Browse allows you to go through a list of items in some specified order:
Browse by Community/Collection takes you through the communities in alphabetical order and allows you to see the subcommunities and collections within each community.
Browse by Title allows you to move through an alphabetical list of all titles of items in DSpace.
Browse by Author allows you to move through an alphabetical list of all authors of items in DSpace.
Browse by Subject allows you to move through an alphabetical list of subjects assigned to items in DSpace.
Browse by Date allows you to move through a list of all items in DSpace in reverse chronological order.
| SEARCH | top |
To search all of DSpace, use the yellow search box at the top of the navigation bar on the left (or the search box in the middle of the home page)

To limit your search to a specific community or collection, navigate to that community or collection and use the search bar on that page.
DSpace uses the Jakarta Lucene search engine. Here are some search hints:
What is searched in the general keyword search (yellow box)
The word(s) you enter in the search box will be searched against the title, author, subject abstract, series, sponsor and identifier fields of each item's record.If your site is enabled for full-text searching, the text you entered will also be searched against the full text of all archived documents. For more information on full-text searching please contact your DSpace Administrator.
What is not searched - Stop Words
The search engine ignores certain words that occur frequently in English, but do not add value to the search. These are:"a", "and" , "are" , "as" , "at" , "be" , "but" , "by" , "for" , "if" , "in" , "into",
"is" ,"it" ,"no" , "not" , "of" , "on" , "or" , "such", "the" , "to" , "was"
Truncation
Use an asterisk (*) after a word stem to get all hits having words starting with that root, for example:
will retrieve selects, selector, selectman, selecting.
Stemming
The search engine automatically expands words with common endings to include plurals, past tenses ...etc.Phrase Searching
To search using multiple words as a phrase, put quotation marks (") around the phrase.

Exact word match
Put a plus (+) sign before a word if it MUST appear in the search result. For instance, in the following search the word "training" is optional, but the word "dog" must be in the result.
Eliminate items with unwanted words
Put a minus (-) sign before a word if it should not appear in the search results. Alternatively, you can use NOT. This can limit your search to eliminate unwanted hits. For instance, in the search
or
you will get items containing the word "training", except those that also contain the word "cat".
Boolean searching
The following Boolean operators can be used to combine terms. Note that they must be CAPITALIZED !
AND - to limit searches to find items containing all words or phrases combined with this operator, e.g.
will retrieve all items that contain BOTH the words "cats" and "dogs".
OR - to enlarge searches to find items containing any of the words or phrases surrounding this operator
will retrieve all items that contain EITHER the words "cats" or "dogs".
NOT - to exclude items containing the word following this operator, e.g.
will retrieve all items that contain the word "training" EXCEPT those also containing the word "cat".
Parentheses can be used in the search query to group search terms into sets, and operators can then be applied to the whole set, e.g.
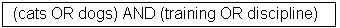
| ADVANCED SEARCH | top |
The advanced search page allows you to specify the fields you wish to search, and to combine these searches with the Boolean "and", "or" or "not".
You can restrict your search to a community by clicking on the arrow to the right of the top box. If you want your search to encompass all of DSpace, leave that box in the default position.
Then select the field to search in the left hand column and enter the word or phrase you are searching in the right hand column. You can select the Boolean operator to combine searches by clicking on the arrow to the right of the "AND" box.
Note: You must use the input boxes in order. If you leave the first one blank your search will not work.
| SUBJECT CATEGORY SEARCH | top |
A controlled vocabulary is a set of terms which form a dictionary of descriptions of particular types of content or subject matter. These are maintained by standards bodies in order to standardise the way that similar materials are categorised in archives. This aids searching by increasing the likelihood that the relevant materials will be returned by the user's search.
Filtering the category list will remove from the list any terms which do not match the filter. The remaining terms are any category or sub category which contains the filter term anywhere in the heirarchy. Expanding each category will show you which terms (or sub terms) did match the filter.
To search the archive items by the subject category, check as many boxes next to the categories as necessary, before clicking "Search...". The search will return all items that either match the categories selected exactly, or which are categorised underneath a higher level category. Clicking on the "+" next to the category will expand the tree to show you what refinements are available for your selected category.
| COMMUNITIES | top |
The DSpace content is organized around Communities which can correspond to administrative entities such as schools, departments, labs and research centers. Within each community there can be an unlimited number subcommunities and an unlimited number of collections. Each collection may contain an unlimited number of items. This organization gives DSpace the flexibility to accommodate differing needs of communities by allowing them to
Each community has its own entry page displaying information, news and links reflecting the interests of that community, as well as a descriptive list of collections within the community.
| COLLECTIONS | top |
Communities can maintain an unlimited number of collections in DSpace. Collections can be organized around a topic, or by type of information (such as working papers or datasets) or by any other sorting method a community finds useful in organizing its digital items. Collections can have different policies and workflows.
Each DSpace collection has its own entry page displaying information, news and links reflecting the interests of users of that collection.
For general information and news about DSpace, visit the DSpace Website.
Contents | Browse | Search | Communities | Collections